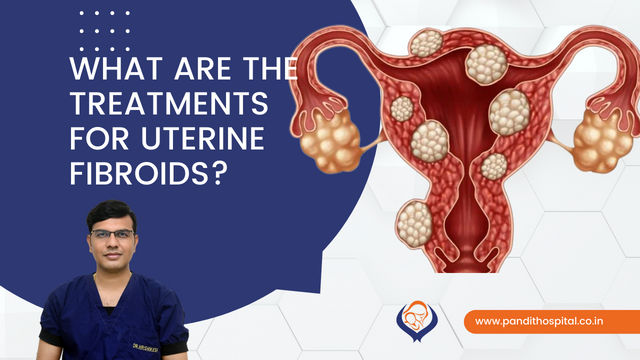
Uterine Fibroids are the most common female reproductive system cancers. They are noncancerous growths that form in or near the uterus. The growths vary in size and are composed of muscle and fibrous tissues. Although not all fibroid cases are detected, it is estimated that 20-50 percent of women of reproductive age have fibroid.
Are uterine fibroids dangerous?
No. As they are not a cancerous growth and can be treated. But don’t ignore the symptoms of uterine fibroids. Most women with fibroid experience no symptoms. But for 25% of women, some symptoms will occur. In those that do, symptoms can be influenced by the location, size and number of fibroids. They vary in size, ranging from microscopic seedling-sized tumors to weighty outgrowths capable of disfiguring the uterus. While some women develop just a single fibroid, others develop a cluster.
What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
Typical symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, menstrual periods lasting more than a week, pelvic pressure or pain, frequent urination, difficulty in emptying the bladder, constipation and backache or leg pains.
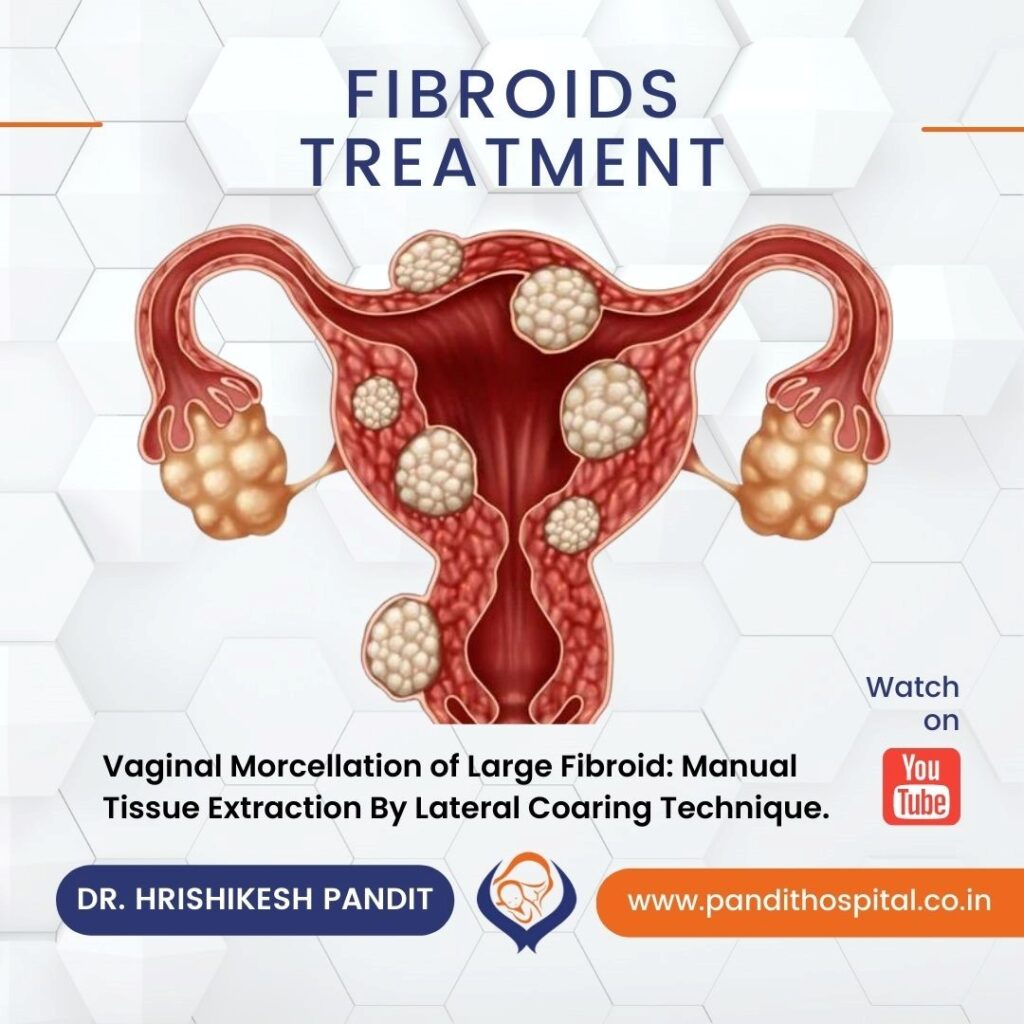
What are the causes of uterine fibroids?
- Genetic Distinction
Fibroids frequently contain genes that are genetically unique from the quality and character of normal uterine muscle cells.
- Hormonal Effects
Fibroids are thought to be associated to the generation of the two main female hormones, estrogen and progesterone. This is because fibroids have more estrogen and progesterone receptors than typical uterine cells. Because of the decline in hormone synthesis, the occurrence and impact of fibroids naturally decreases after menopause.
- Congenital Characteristics
If your sister or mother was diagnosed with fibroids, you are likely to have them as well.
- Environmental Factors
If you had menarche early, are currently using birth control pills, are fat, have a vitamin D deficiency, or drink alcohol, fibroids have a larger chance of appearing. Fibroids grow in a variety of ways; some grow quickly, while others cease growing early.
What are the treatments for uterine fibroids?
- Expectant Management:
This strategy, also known as cautious waiting, is best suited for women who have few or no symptoms. Fibroids, which are non-cancerous and normally do not interfere with conception, tend to shrink on their own after menopause.
- Medication Plan:
A number of medication plans exist for fibroids, many of them pointed at regulating your menstrual cycle, managing excessive menstrual bleeding and minimizing pelvic pain. While medications do not eradicate fibroids, they may play a role in diminishing them.
- Non-invasive option:
There are several non-invasive surgical approaches for removing uterine fibroids that are performed using ultrasound.
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), is an FDA approved, non-surgical, minimally-invasive procedure that reduces the bleeding, pain and other symptoms of uterine fibroids in 90% of women who have the treatment.
- Minimal invasive surgery or laparoscopic surgery for uterine fibroids removal:
Surgery is a more definitive treatment. Surgery can involve only removal of the fibroid (myomectomy) or removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) depending on age and reproductive status of the women. It can be done either by a large incision in the abdomen to access the uterus or laparoscopically, using a few small incisions into which surgical tools and a camera are inserted. Advantages of laparoscopic procedure are lesser painful, faster recovery, cosmesis, lesser post op adhesions and hence better preservation of fertility.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is the best option for uterine fibroids for the women after menopause.
What is recovery time after uterine fibroids surgery?
For hysterectomy patients, it is around 6-8weeks and for myomectomy patients, it is around 4-6 weeks.
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit is the pioneer pf 3D laparoscopy technique in Ahmednagar. His experience and skill makes him one of the best laparoscopic surgeon in India.
At Pandit Hospital, you are in safe hands!
To consult Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit, Click Below,
Pandit Hospital – Best Maternity care center in Ahmednagar
LET’S SEE OUR INTRO VIDEO
At Pandit Hospital, we provide all the maternity services from antenatal to postnatal period under one roof
Let's Connect!!
Nagar - Pathardi Road, Bhingar, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India 414002
0241-2441717 / 0241-2442344
info.pandithospital@gmail.com
About author:
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit:
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit is one of the best obstetrician and gynecologist in India. He is also a well-renowned Laparoscopic surgeon. He obtained his MS (Ob Gyn) degree from the prestigious Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences. He has also done fellowship and diploma courses in laparoscopic surgeries and cancer treatment from Tata Hospital and Keil University, Germany. His surgical cases, papers and videos has been chosen in many international forums of gynecology.

Why Pandit Hospital?
At Pandit Hospital, we are always working hard to provide its patients with the highest level of medical innovation and patient care. With the aim of delivering complete maternity & gynecological care under one roof with the help of all contemporary amenities and cutting-edge medical equipment. Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit has a vision to bring the best of facilities regarding laparoscopy surgeries in the city of Ahmednagar. He is the pioneer of 3D Laparoscopy technology is Ahmednagar.
Latest Articles
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit is one of the best laparoscopy surgeons in India. His determination to bring 3D Laparoscopy technology to Ahmednagar has eventually helped so many patients. Read the latest articles by Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit on Gynecology, gastric issues, and health tips for mothers during pregnancy.
Laparoscopic Cerclage is done for cervical insufficiency or early abortion history. Consult Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit to know more about it. Excellent results in High Risk Pregnancies. Watch video on YouTube.
At Pandit Hospital, Ahilyanagar, we provide advanced maternity care with state-of-the-art 3D laparoscopy and sonography services to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
Pandit Hospital, led by Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit, offers 3D laparoscopic treatments including Laparoscopic Vaginoplasty, to restore both form and function in women seeking vaginal reconstruction in india.
FAQ
You should consult a doctor during the first 6 to 8 weeks of your pregnancy, or when your period is 2 to 4 weeks late.
If your contractions are 5 minutes apart, lasting for 1 minute, for 1 hour or longer, it’s time to head to the hospital.
Doctors recommend an infertility evaluation if you have not gotten pregnant after 1 year of having regular sexual intercourse without using birth control. If you are older than 35, an evaluation is recommended after 6 months of trying.
Yes, You can. But most babies need 39 weeks to develop fully. Induced or planned delivery before that time—without a valid medical reason—is not in the best interest of the baby or the mother. After 39 weeks you can plan delivery.
Women who are 21 to 29 should have a Pap test alone every 3 years. HPV testing alone can be considered for women who are 25 to 29, but Pap tests are preferred. Women who are 30 to 65 have three options for testing. They can have a Pap test and an HPV test (co-testing) every 5 years. They can have a Pap test alone every 3 years. Or they can have HPV testing alone every 5 years.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a safe and suitable procedure for chosen patients. It affords patients advantages like less peri-operative morbidity, better life quality, shorter hospitalization time, and faster return to activity.
Schedule a doctor’s visit if you have: Greenish, yellowish, thick or cheesy vaginal discharge; Strong vaginal odor; Redness, itching, burning or irritation of your vagina or the area of skin that surrounds the vagina and urethra (vulva); Bleeding or spotting unrelated to your period.
Painless delivery can be achieved using a form of regional anesthesia that provides pain relief during natural labor. Epidural anesthesia is administered through an injection on the lower back of the mother. The drug takes about 10-15 minutes to take effect.
Even in severe cases of endometriosis, most can be treated with laparoscopic surgery. In laparoscopic surgery, your surgeon inserts a slender viewing instrument (laparoscope) through a small incision near your navel and inserts instruments to remove endometrial tissue through another small incision.
The HPV vaccine is recommended for routine vaccination at the age of 11 or 12 years. (Vaccination can be started at age 9.) It is also recommended that vaccination for everyone through age 26 years if not adequately vaccinated when younger. HPV vaccination is given as a series of either two or three doses, depending on age at initial vaccination.