As per World Health Organization (WHO), around 10% of women of reproductive age group (around 190 million) are affected by endometriosis globally.
One of the top 3 factors that prevent a woman from becoming pregnant is endometriosis. Women with endometriosis who struggle with infertility account for 30–40% of all cases. One of the top 10 most painful medical diseases recently was Endometriosis. Mostly undergoes misdiagnosed for many years causing further problems.
What is endometriosis?
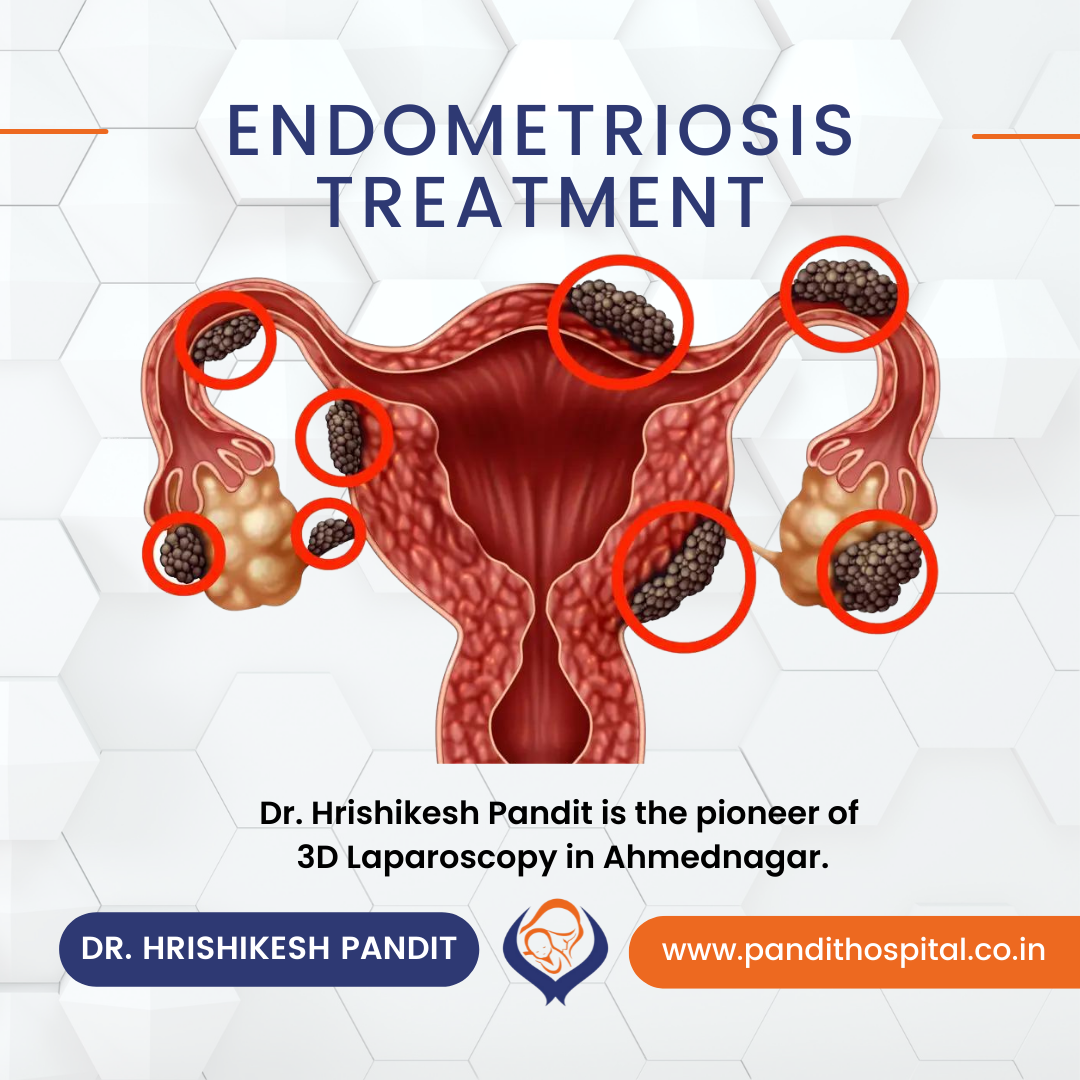
Endometrium, the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus or womb. It is shed off with the blood during periods, grows outside the uterus in this disease and is seen to affect the ovaries, intestines, urinary bladder, the lining of your pelvis, and may even spread to distant sites like the lungs, etc.
What causes pain in endometriosis?
Endometrial tissue that has been positioned incorrectly continues to behave as it would, thickening, breaking, and bleeding much like the uterine lining does each month.
Now that regular periods are flushing out the blood and abnormal tissue, there is no route for them to escape the body. Therefore, during each cycle, this tissue and blood become trapped inside the body, irritating the surrounding tissues and causing nodules to grow that stick to the surrounding organs, create discomfort, and impair the function of the organ in question.
The body also understands that this growth. So it attempts to remove these tissues by igniting an inflammatory response against these tissues, which results in excruciating pain, scarring, and internal tissue and organ destruction.
What are the risk factors of endometriosis?
- Genetic predisposition
- Menstrual cycle initiation at young age.
- No pregnancy
- Associated diseases like fibroids etc.
What are the symptoms of endometriosis?
- Painful period
- Painful intercourse
- Excessive bleeding during periods
- Infertility
- Pain during bowel movements
- Chronic pelvic pain, groin pain or even chest pain in some cases.
How to diagnose the endometriosis?
After thorough medical examination and history, ultrasonography and MRI can be done to locate the tissue.
Diagnostic laparoscopy surgery remains the gold standard procedure to detect endometrial tissue.
What are the stages of endometriosis?
Stage 1: Minimal – In minimal endometriosis, there are small lesions or wounds and shallow endometrial implants on your ovaries. There may also be inflammation in or around your pelvic cavity.
Stage 2: Mild – Mild endometriosis involves light lesions and shallow implants on the ovaries and the pelvic lining.
Stage 3: Moderate – Moderate endometriosis involves many deep implants on your ovaries and pelvic lining. There can also be more lesions.
Stage 4: Severe – The most severe stage of endometriosis involves many deep implants on your pelvic lining and ovaries. There may also be lesions on your fallopian tubes and bowels. There can also be cysts on one or both of your ovaries.
What are the treatments for endometriosis?
There is currently no cure for endometriosis, but there are treatment options for related pain and infertility.
Treatment for Pain in endometriosis:
- Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy is used to treat endometriosis-associated pain. Hormones come in the form of a pill, a shot or injection, or a nasal spray.
Hormone treatments stop the ovaries from producing hormones, including estrogen, and usually prevent ovulation. This may help slow the growth and local activity of both the endometrium and the endometrial lesions. Treatment also prevents new areas and scars (adhesions) from growing, but it will not make existing adhesions go away.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) medicines stop the production of certain hormones to prevent ovulation, menstruation, and the growth of endometriosis.
Oral contraceptives, or birth control pills. These helps make a woman’s period lighter, shorter, and more regular.
Progesterone and progestin, taken as a pill, by injection, or through an intrauterine device (IUD), improve symptoms by reducing a woman’s period or stopping it completely. This also prevents pregnancy.
Danazol (also called Danocrine®) treatment stops the release of hormones that are involved in the menstrual cycle.
- Pain Medications like NSAIDs.
- Surgery:
Laparoscopy remains the gold standard surgical treatment for endometriosis. With help of laparoscope surgeon performs two important steps to remove the lesions, which is a process called excising & destroy the lesions with intense heat and seal the blood vessels without stitches, a process called cauterizing or vaporizing.
If the expansion on the tissue is severe then laparoscopic hysterectomy may also be required to remove entire uterus along with the ovaries.
Surgery to sever pelvic nerves. If the pain is in the center of the abdomen, healthcare providers may recommend cutting nerves in the pelvis to lessen the pain. This can be done during either laparoscopy or laparotomy.
Presacral neurectomy severs the nerves connected to the uterus.
Laparoscopic uterine nerve ablation (LUNA) severs nerves in the ligaments that secure the uterus.
Treatments for Infertility Related to Endometriosis:
If pregnancy does not occur after laparoscopic treatment, in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be the best option to improve fertility. Taking any other hormonal therapy usually used for endometriosis-associated pain will suppress ovulation and delay pregnancy.
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit is the pioneer pf 3D laparoscopy technique in Ahmednagar. His experience and skill makes him one of the best laparoscopic surgeon in India.
At Pandit Hospital, you are in safe hands!
To consult Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit, Click Below,
Pandit Hospital – Best Maternity care center in Ahmednagar
LET’S SEE OUR INTRO VIDEO
At Pandit Hospital, we provide all the maternity services from antenatal to postnatal period under one roof
Let's Connect!!
Nagar - Pathardi Road, Bhingar, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India 414002
0241-2441717 / 0241-2442344
info.pandithospital@gmail.com
About author:
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit:
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit is one of the best obstetrician and gynecologist in India. He is also a well-renowned Laparoscopic surgeon. He obtained his MS (Ob Gyn) degree from the prestigious Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences. He has also done fellowship and diploma courses in laparoscopic surgeries and cancer treatment from Tata Hospital and Keil University, Germany. His surgical cases, papers and videos has been chosen in many international forums of gynecology.

Why Pandit Hospital?
At Pandit Hospital, we are always working hard to provide its patients with the highest level of medical innovation and patient care. With the aim of delivering complete maternity & gynecological care under one roof with the help of all contemporary amenities and cutting-edge medical equipment. Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit has a vision to bring the best of facilities regarding laparoscopy surgeries in the city of Ahmednagar. He is the pioneer of 3D Laparoscopy technology is Ahmednagar.
Latest Articles
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit is one of the best laparoscopy surgeons in India. His determination to bring 3D Laparoscopy technology to Ahmednagar has eventually helped so many patients. Read the latest articles by Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit on Gynecology, gastric issues, and health tips for mothers during pregnancy.
Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit answers common questions about Laparoscopic Radical Hysterectomy at Pandit Hospital’s 3D Laparoscopy Center.
Laparoscopic Cerclage is done for cervical insufficiency or early abortion history. Consult Dr. Hrishikesh Pandit to know more about it. Excellent results in High Risk Pregnancies. Watch video on YouTube.
At Pandit Hospital, Ahilyanagar, we provide advanced maternity care with state-of-the-art 3D laparoscopy and sonography services to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
FAQ
You should consult a doctor during the first 6 to 8 weeks of your pregnancy, or when your period is 2 to 4 weeks late.
If your contractions are 5 minutes apart, lasting for 1 minute, for 1 hour or longer, it’s time to head to the hospital.
Doctors recommend an infertility evaluation if you have not gotten pregnant after 1 year of having regular sexual intercourse without using birth control. If you are older than 35, an evaluation is recommended after 6 months of trying.
Yes, You can. But most babies need 39 weeks to develop fully. Induced or planned delivery before that time—without a valid medical reason—is not in the best interest of the baby or the mother. After 39 weeks you can plan delivery.
Women who are 21 to 29 should have a Pap test alone every 3 years. HPV testing alone can be considered for women who are 25 to 29, but Pap tests are preferred. Women who are 30 to 65 have three options for testing. They can have a Pap test and an HPV test (co-testing) every 5 years. They can have a Pap test alone every 3 years. Or they can have HPV testing alone every 5 years.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a safe and suitable procedure for chosen patients. It affords patients advantages like less peri-operative morbidity, better life quality, shorter hospitalization time, and faster return to activity.
Schedule a doctor’s visit if you have: Greenish, yellowish, thick or cheesy vaginal discharge; Strong vaginal odor; Redness, itching, burning or irritation of your vagina or the area of skin that surrounds the vagina and urethra (vulva); Bleeding or spotting unrelated to your period.
Painless delivery can be achieved using a form of regional anesthesia that provides pain relief during natural labor. Epidural anesthesia is administered through an injection on the lower back of the mother. The drug takes about 10-15 minutes to take effect.
Even in severe cases of endometriosis, most can be treated with laparoscopic surgery. In laparoscopic surgery, your surgeon inserts a slender viewing instrument (laparoscope) through a small incision near your navel and inserts instruments to remove endometrial tissue through another small incision.
The HPV vaccine is recommended for routine vaccination at the age of 11 or 12 years. (Vaccination can be started at age 9.) It is also recommended that vaccination for everyone through age 26 years if not adequately vaccinated when younger. HPV vaccination is given as a series of either two or three doses, depending on age at initial vaccination.